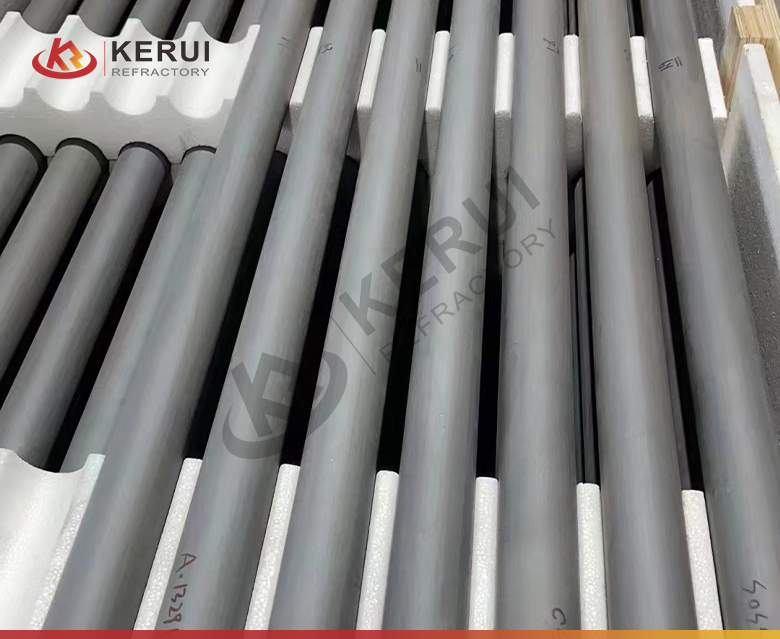
Silicon Carbide Roller
Silicon carbide rollers are crucial in high-temperature kilns and furnaces, serving industries like ceramics, glass production, and steel manufacturing. They withstand harsh conditions, providing smooth material movement through thermal systems.
-
85%
sic (>)
-
3.02g/cm²
Bulk Density(>)
-
1380℃
Max Service Temp
-
45W/m·K(1200℃)
Thermal Conductivity



Technical Data of Kerui Silicon Carbide Roller
| Item | SiO₂-SiC | SiSiC/RBSiC | R-SiC | Si3N4-SiC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiC % | >85 | 90~92 | >99 | ≥75 |
| Density g/cm3 | 2.65~2.75 | >3.02 | 2.65~2.75 | 2.65~2.85 |
| Porosity % | 15~16 | <0.1 | 15-18 | 13-15 |
| Bending strength (20℃)Mpa | 90~100 | 260 | 80~100 | 160-180 |
| Bending strength (1200℃)Mpa | 100~110 | 280 | 90~110 | 170-180 |
| compressive strength (20℃)Mpa | ≥300 | 900 | ≥300 | 580 |
| Hardness Kg/mm2 | 1800~2000 | 2400 | 1800~2000 | 2000-3000 |
| Thermal Conductivity (1200℃)w.m-1.k-1 | 35~36 | 45 | 36 | 19.6 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion(1200℃) α×10-6/C | 4.6 | 4.5 | 4.6 | 4.7 |
| Maximum operation temperature ℃ | 1500 | 1380 | 1650 | 1550 |
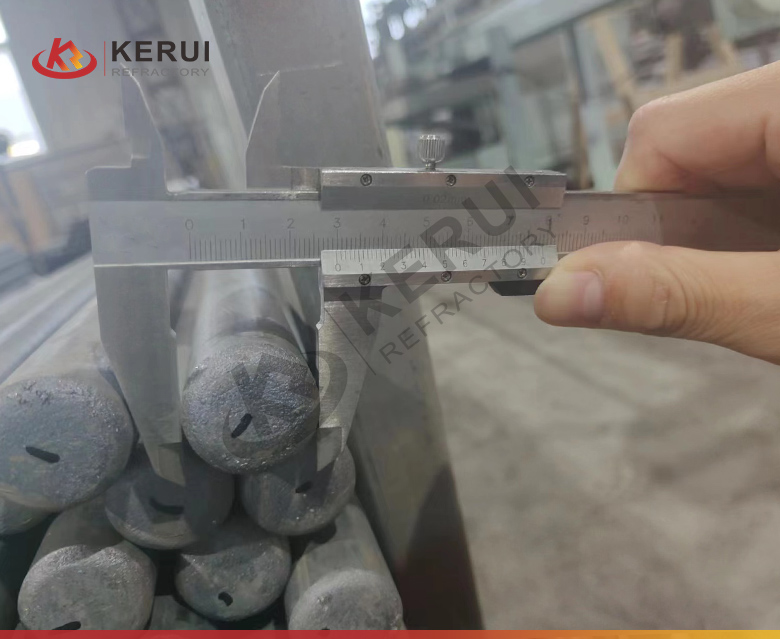
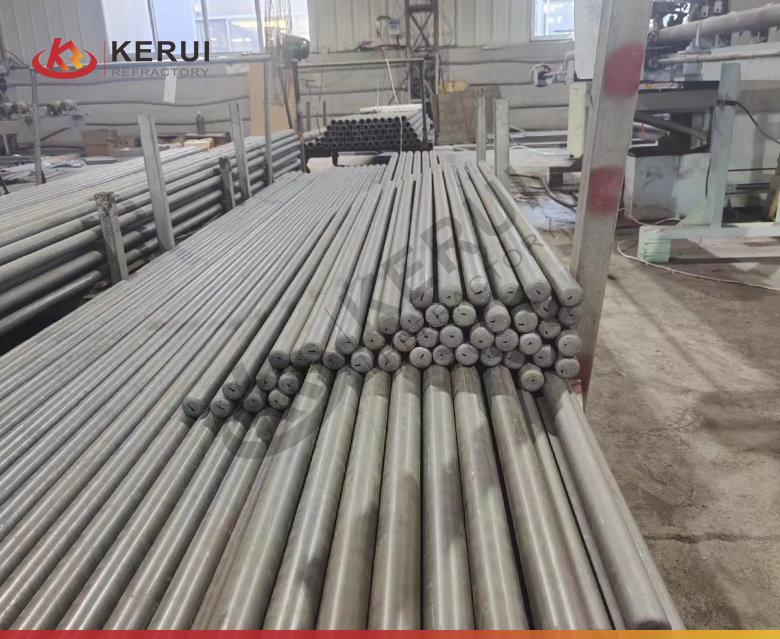



Features of Kerui Silicon Carbide Roller
- High Heat Resistance: SiC rollers can function at temperatures up to 1600°C (2900°F) without any degradation, making them ideal for continuous firing and cooling applications.
- Wear Resistance: These rollers are highly resistant to abrasion and wear, ensuring a long service life even in high-load and high-stress applications.
- Low Thermal Expansion: Silicon carbide rollers have a very low thermal expansion coefficient, meaning they maintain their shape and size even under extreme temperatures.
- Smooth Operation: Their precise construction ensures smooth and consistent material movement through kilns and furnaces.
- Corrosion and Chemical Resistance: These rollers are resistant to most acids, alkalis, and slags, ensuring that they maintain operational efficiency in aggressive environments.
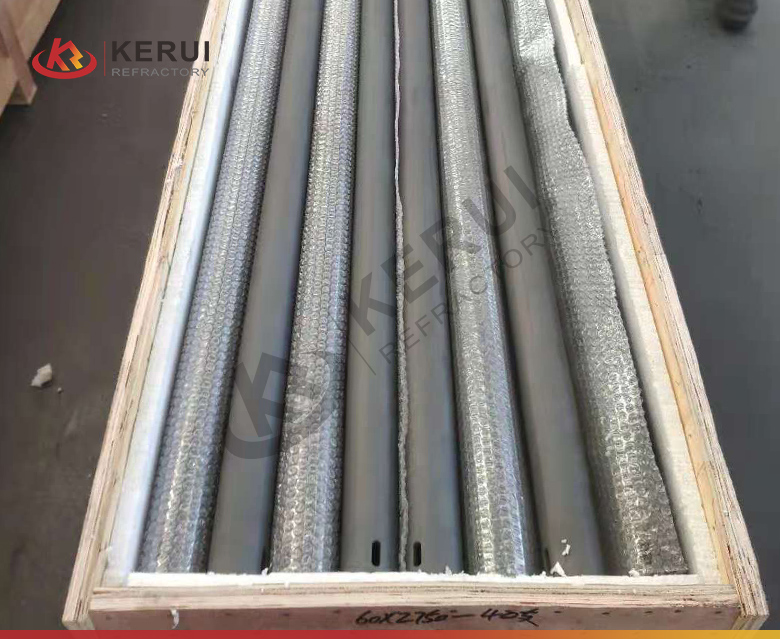
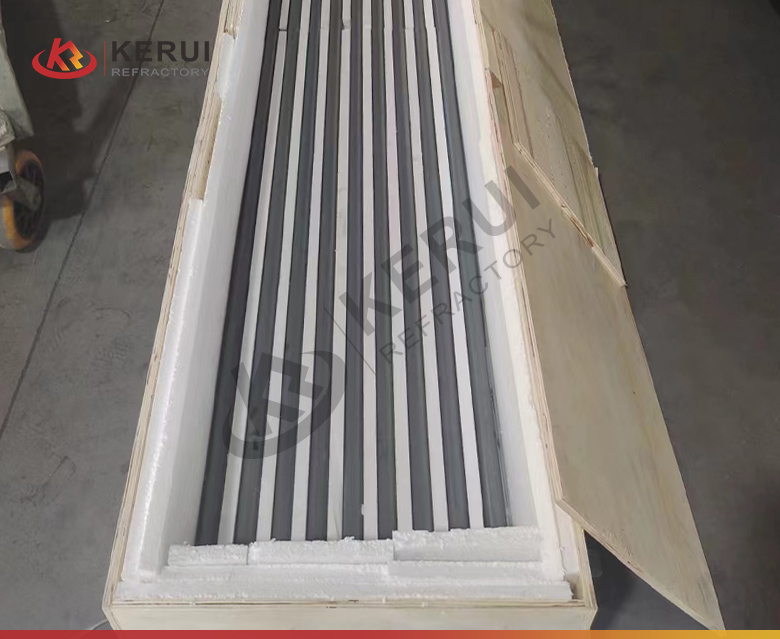



Main Uses of Kerui Silicon Carbide Roller
Kiln Roller Conveyors:
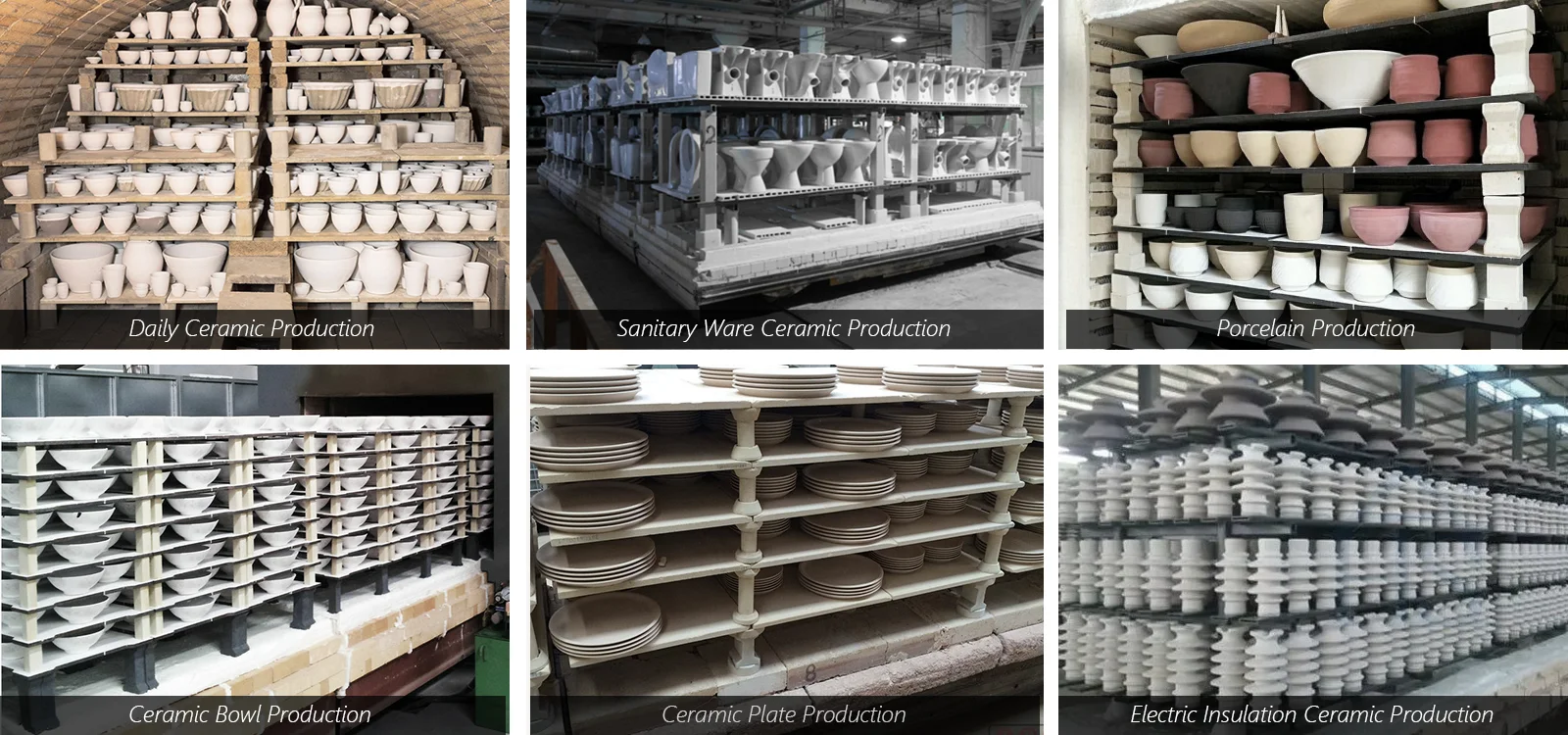
Silicon carbide rollers are commonly used to transport materials such as ceramics and glass through high-temperature kilns.
Ceramic Firing:
Used as kiln furniture in ceramic firing processes to support and transport ceramic products through the furnace.
Glass Manufacturing:
Employed in glass melting and molding processes where they withstand both high temperatures and corrosive conditions.
Steel Reheating Furnaces:
Utilized in reheating furnaces to transport steel billets, ensuring consistent movement and temperature distribution.