It is well known that refractory bricks can be divided into soft brick and hard brick. Although there is only one-word difference, soft brick vs hard brick is totally different. Do you want to know how to distinguish them? Do you want to know which one of them can meet your needs better? The following article will give you answers.
What Are Soft Brick and Hard Brick?
Soft Brick
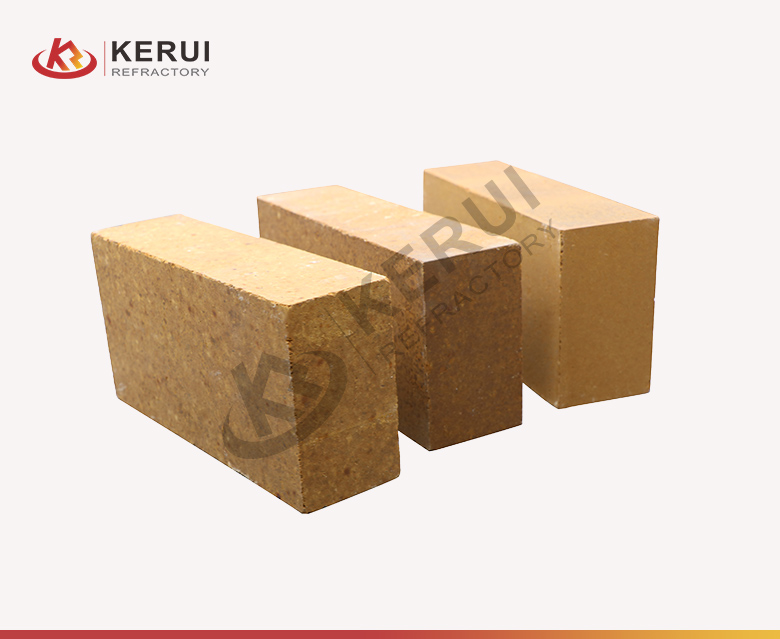
Soft brick is also known as insulation fire brick (IFB) or lightweight brick. Because of its lightweight and uniform pore structure, this brick is named soft brick. It is made of refractory clay, alumina, and the appropriate amount of organic filling. Generally, the soft brick can withstand the temperature of 1093-1760℃ (1994-3200℉).
Main soft bricks: lightweight high-alumina brick, clay brick, silica brick, lightweight clay brick, mullite brick, alumina bubble brick, etc.
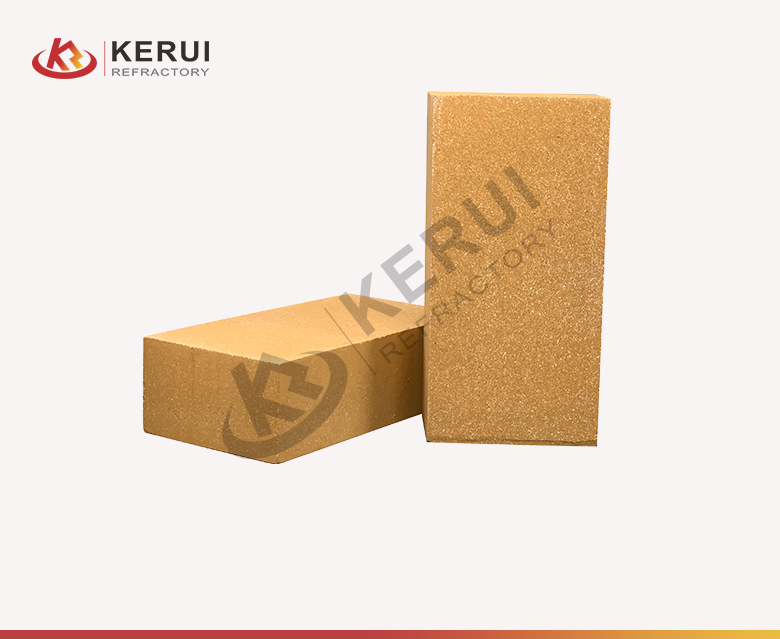
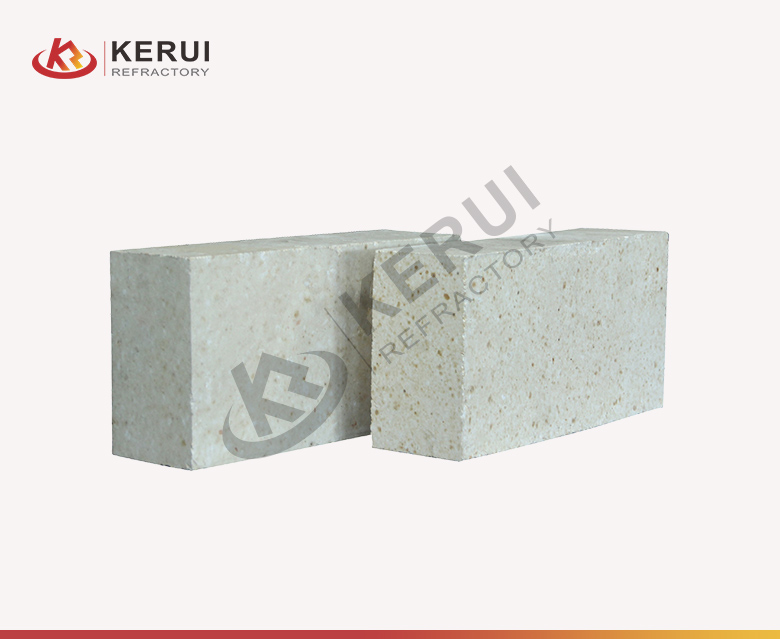



Hard Brick
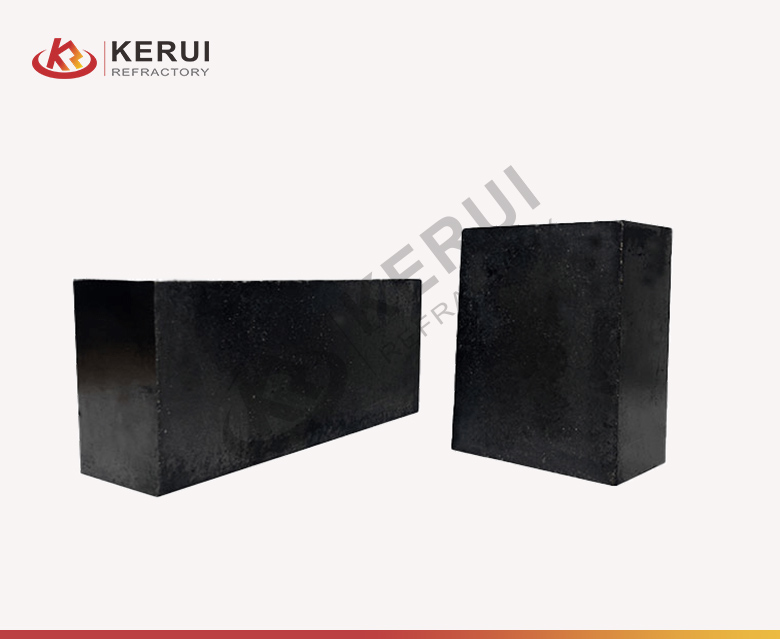
Hard brick is also known dens brick. As its name says that hard brick is denser than soft brick. Hard brick is mainly made of high alumina and silica, which is formed by high-pressure molding, drying and high-temperature sintering. The maximum heat-resistant temperature of the brick can reach 1900℃ (3452℉).
Main hard bricks: heavy high-alumina brick, magnesia brick, AZS brick, magnesia carbon brick, alumina silica brick, etc.



Performance Comparison of Soft Brick vs Hard Brick
Thermal Conductivity
Hard brick holds fewer pores than soft brick and are denser. This means it has higher thermal conductivity. As a result, hard brick is less effective in insulating.
Soft brick has lower thermal conductivity than hard brick. There are a large number of gas pores in the soft brick. These pores can hinder heat conduction to reduce thermal conductivity.
Fire Resistance
Hard brick has a higher density and weight. Thus, it has excellent fire resistance. Their denser composition allows them to store more thermal energy before reaching a critical temperature.
Conversely, soft insulation brick has slightly lower fire resistance. Soft refractory bricks have a lower density. It has a poor ability to absorb heat evenly. Therefore it is more susceptible to thermal shock.
Mechanical Strength
Materials such as alumina, magnesia, or silica are used to make hard bricks, which are denser and heavier. Therefore, hard brick can withstand greater mechanical stress.
In contrast, soft brick has low mechanical strength. Therefore it cannot be used in load-bearing structures.


Different Uses Between Soft Brick vs Hard Brick
Uses of Soft Brick
Because of their good insulating properties, soft brick is often used to furnace insulation such as ceramic furnaces, glass furnaces, heat treatment furnaces, etc. At the same time, soft bricks are also commonly used in the ceramic industry. Because they can be easily shaped and cut to fit a specific space.
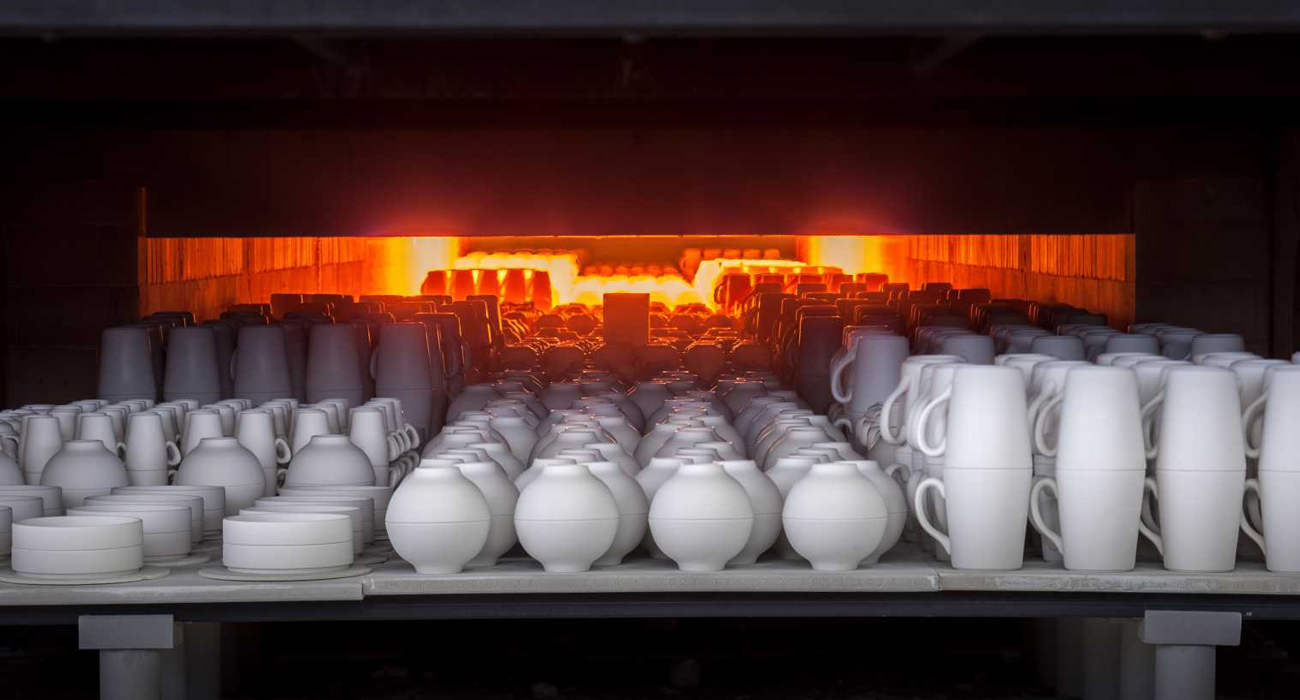

Uses of Hard Brick
The dense structure brings hard brick with excellent performance. It can withstand the intense combustion temperature and the thermal expansion inside the boiler. Therefore, this kind of brick is most commonly found in the parts that are in direct contact with the flame such as large kilns, incinerators, and burner ports.
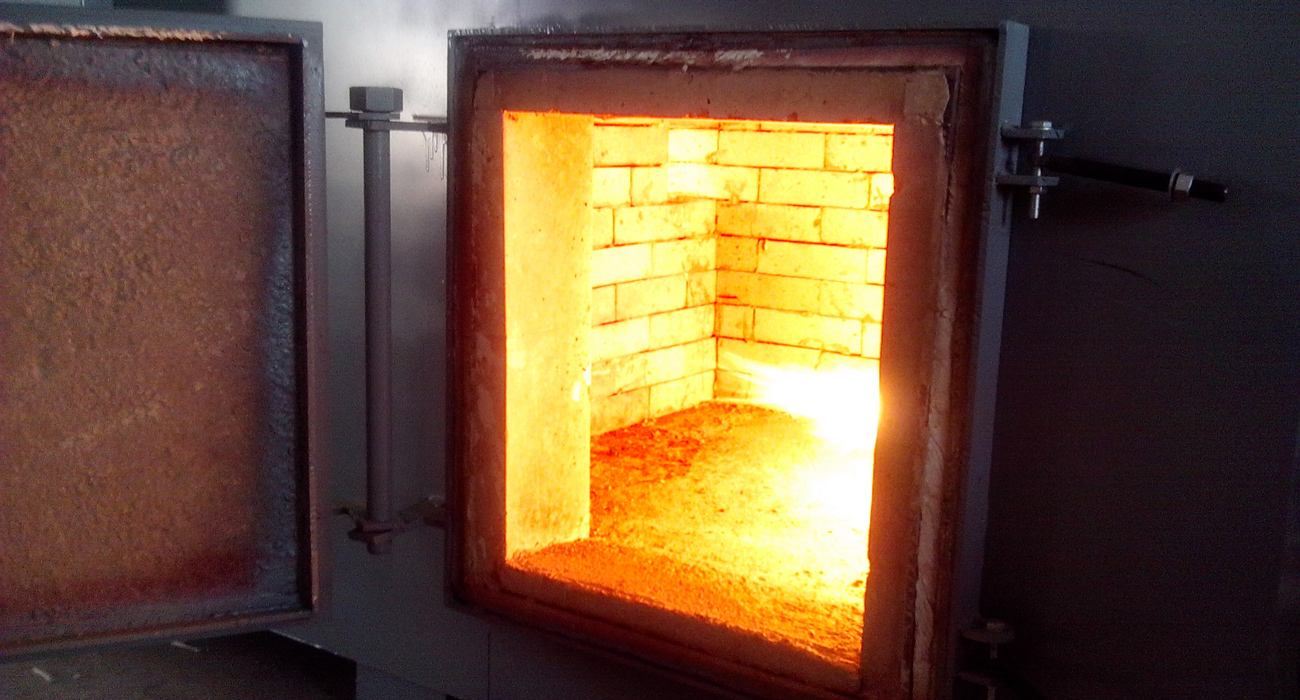

Conclusion
Different compositions give completely different properties to soft brick and hard brick. Of course, in the application, each specific requirement should be considered to select the appropriate brick type accordingly. All in all, soft bricks are excellent in insulating. Hard bricks are more suitable for areas exposed directly to thermal and mechanical stress.
Kerui can supply top-quality soft brick and hard brick. If you still feel confused about which of these two bricks is more suitable for your equipment, Kerui will give your more details. Its professional technician also can make provide a package plan for you.